Authors: Prof. Talia Golan , Dr. Ofer Purim, Prof. Danny Rosin, Dr. Eli Sapir, Prof. Moshe Gatt, Dr. Tomer Charas, Dr. Ilya Iofin, Prof. Ido Wolf, Bozhena Haikin , Dr. Daniel A. Vorobiof.
Researched by: investigators from Sheba Medical Center, Shaarei Tzedek Medical Center, Assuta Ashdod University Medical Center, Hadassah Medical Center, Rambam Hospital, Ichilov Hospital, Israel; Mount Sinai Medical Center, New York, NY, and Belong.Life.
Poster presented and Abstract Published in ESMO’s Annual Congress Abstract Book 2024 (doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.08.1929)
Background
The first conversational AI Cancer mentor app was recently launched by Belong.life, a global oncology social network for cancer patients (pts) and caregivers. The app objectives are to provide uninterrupted support, patient education and guidance with empathetic, relevant information in cancer management. Belong’s unique and large datasets of pts to physicians and pts to pts interactions provide the basis for the AI platform, adding information from current guidelines, supplying solid up to date data with wide understanding of pts diverse cancer journeys.
Methods
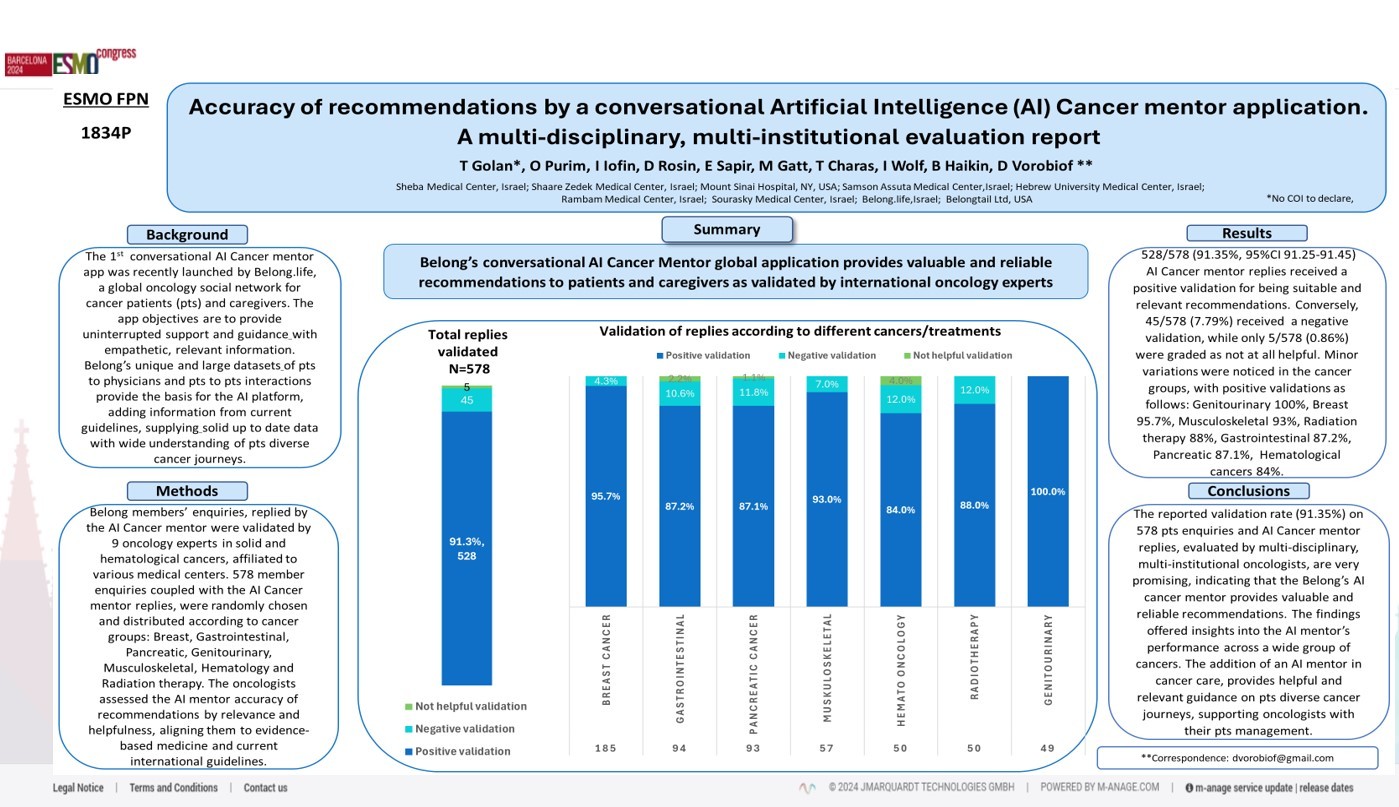
Belong members enquiries, replied by the AI Cancer mentor were validated by 9 oncology experts in solid and haematological cancers, affiliated to various medical centres. 578 member enquiries coupled with the AI Cancer mentor replies, were randomly chosen and distributed according to cancer groups: Breast, Gastrointestinal, Pancreatic, Genitourinary, Musculoskeletal, Haematology and Radiation therapy. The oncologists assessed the AI mentor accuracy of recommendations by relevance and helpfulness, aligning them to evidence-based medicine and current international guidelines.
Results
527/578 (91.18%) AI Cancer mentor replies received a positive validation for their suitable and relevant recommendations. Conversely, 46/578 (7.96%) received a negative validation, while only 5/578 (0.86%) graded as not helpful. Minor variations were noticed in the cancer groups, with positive validations as follows: Genitourinary 100%, Breast 95.7%, Pancreatic 92%, Musculoskeletal 91.2%, Radiation therapy 88%, Gastrointestinal 86.4%, Haematological cancers 84%.
Conclusions
The reported accuracy (91.18%) on 578 pts enquiries and AI Cancer mentor replies, evaluated by a multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional oncologist group, are very promising, indicating that the Belong’s AI cancer mentor provides valuable and reliable recommendations. The findings offered insights into the AI mentor’s performance across a wide group of cancers. Based on this report, the addition of an AI mentor in cancer care, provides helpful, relevant guidance on pts diverse cancer journeys, while supporting oncologists in their pts management.
ESMO Poster